Science:研究人员用光来战胜小鼠的健忘症
 2016-05-25来源:未知
2016-05-25来源:未知研究人员说,小鼠的已经丧失稳定并被忘却的记忆仍然可以通过用光激活记忆印迹而被找回;记忆印迹指的是在记忆被编码时特殊的神经元放电模式。这些发现对记忆整合提出了新的阐述;记忆整合是新的、不稳定记忆转变成为稳定、长期记忆的过程。在此之前,研究人员一直想知道记忆整合是否依靠这些记忆痕迹的稳定性。但Tomás Ryan和同事显示,在有着逆行性遗忘的小鼠中情况并非如此。研究人员首先研究了在一种恐惧调适练习中的健康小鼠的海马神经元,并观察到,记忆印迹细胞比非记忆印迹细胞有着更强的突触和更致密的树突棘。他们用一种光敏蛋白来标记那些记忆印迹细胞,并接着在24小时后给他们的某些小鼠注射一种被称作茴香霉素(ANI)的蛋白合成抑制剂。ANI降低了小鼠记忆印迹细胞的突触强度和树突棘密度,导致注射过的小鼠忘却了前一天所经历的恐惧调适。出人意料的是,通过激活在恐惧调适时被标记该光敏蛋白的记忆印迹细胞,Ryan和他的团队能够用光来克服这种逆行性遗忘,并恢复小鼠的恐惧记忆。总之,这些结果提示,编码记忆需要记忆印迹细胞,而在这些细胞中突触的加强在找回记忆的过程中起着某种关键的作用。他们说,研究人员在研究记忆整合时所用的光遗传学方法可能还适用于其它的遗忘症(如阿尔茨海默氏病)实验和临床案例。
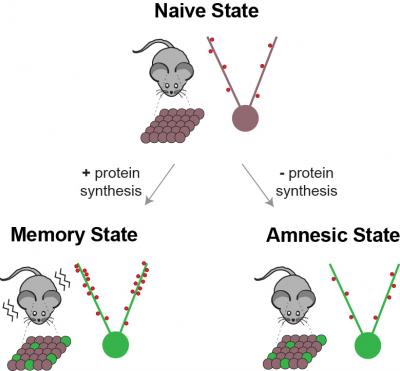
文字说明: 恐惧记忆的行为表达。在初始(未学习的)状态,小鼠没有获得条件特异性的记忆印记。在学习过的记忆状态,小鼠得到了一种突触增强的恐惧记忆印记,它使得小鼠会在恐惧环境中表现出冻住行为。在遗忘状态,蛋白合成抑制在小鼠中导致了被中断的及突触减弱的恐惧记忆印记,使得小鼠在恐惧环境中不再会引起冻住行为。
原文链接:Engram cells retain memory under retrograde amnesia
原文摘要:Memory consolidation is the process by which a newly formed and unstable memory transforms into a stable long-term memory. It is unknown whether the process of memory consolidation occurs exclusively through the stabilization of memory engrams. By using learning-dependent cell labeling, we identified an increase of synaptic strength and dendritic spine density specifically in consolidated memory engram cells. Although these properties are lacking in engram cells under protein synthesis inhibitor–induced amnesia, direct optogenetic activation of these cells results in memory retrieval, and this correlates with retained engramcell–specific connectivity. We propose that a specific pattern of connectivity of engram cells may be crucial for memory information storage and that strengthened synapses in these cells critically contribute to thememory retrieval process.



