Cell子刊:Foxo1调控的NK细胞免疫功能机制
 2016-05-25来源:未知
2016-05-25来源:未知
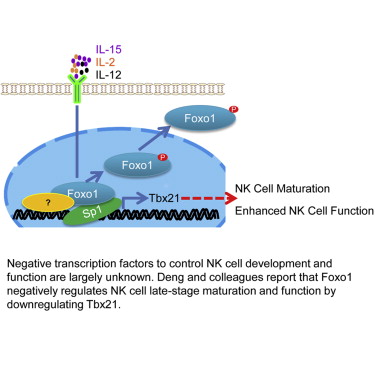
日前,俄亥俄州立大学、第三军医大学等机构的研究人员解析了一个抑制NK细胞成熟和归巢(homing)行为的调控通路。
研究人员对小鼠模型和人类NK细胞进行研究,发现NK细胞的发育和功能受到转录因子Foxo1的负调控。这一发现可以帮助人们开发出新策略,提高自然杀伤细胞对抗癌症和病毒感染的活性。
研究显示,NK细胞的成熟受到Foxo1和Foxo3控制,其中起主要作用的是Foxo1,降低Foxo1的表达可以促进NK细胞成熟。进一步研究表明,Foxo1通过阻断Tbx21基因的转录起作用,Tbx21是NK细胞发育和功能的正调节蛋白。
“癌细胞可以利用这一通路,阻断NK细胞的功能并躲避免疫应答,”文章的通讯作者,俄亥俄州立大学的助理教授Jianhua Yu说。“这项研究为我们提供了增强NK细胞抗肿瘤活性的好机会。”
原文链接:Transcription Factor Foxo1 Is a Negative Regulator of Natural Killer Cell Maturation and Function
原文摘要:Little is known about the role of negative regulators in controlling natural killer (NK) cell development and effector functions. Foxo1 is a multifunctional transcription factor of the forkhead family. Using a mouse model of conditional deletion in NK cells, we found that Foxo1 negatively controlled NK cell differentiation and function. Immature NK cells expressed abundant Foxo1 and little Tbx21 relative to mature NK cells, but these two transcription factors reversed their expression as NK cells proceeded through development. Foxo1 promoted NK cell homing to lymph nodes by upregulating CD62L expression and inhibited late-stage maturation and effector functions by repressing Tbx21 expression. Loss of Foxo1 rescued the defect in late-stage NK cell maturation in heterozygous Tbx21+/− mice. Collectively, our data reveal a regulatory pathway by which the negative regulator Foxo1 and the positive regulator Tbx21 play opposing roles in controlling NK cell development and effector functions.



